Lyngdorf 1120MK speakersLyngdorf bw2 sub. There is an efficiency penalty to this approach.

Class Ab Inverting Amp Uses Two Floating Amplifier Cells Edn
Wide Swing CMOS Configuration Complementary push-pull common source Provides high voltage gain as compared to follower Moderately high output impedance Output swing improved to within an overdrive voltage from the supplies 21 𝑣 𝑉.
Class ab distoetion ay high voltage. Use 12V DC for powering the amplifier. This solves the crossover distortion problem. A 180 Watt Class AB VFA Featuring Ultra Low Distortion.
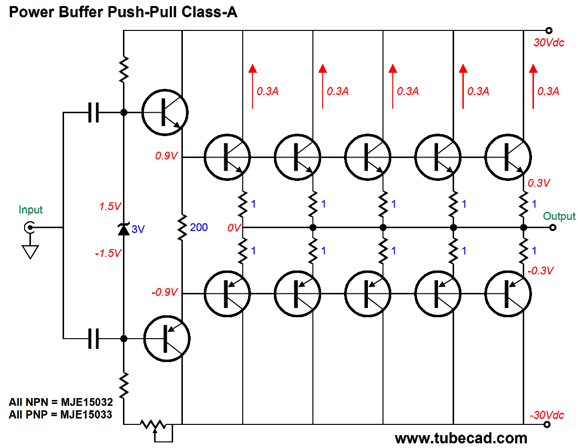
So far we have only talked about push-pull Class A bias. High efficiencygreater than 90. This is understood with the help of below figure.
In class AB each of the push-pull transistors is. High power consumption and significant heat generation. Class AB overcomes the crossover distortion of Class B by biasing the devices slightly into the cut-off region with 180⁰ of conduction.
The e-Amp is a 180 Watt RMS very conservatively rated into 8 Ω fully balanced symmetrical FBS amplifier featuring an emitter follower triple EFT bipolar. A Class AB 150 watt amplifier channel with 01 amp bias will idle at about 10 watts. This of course will result in more heat dissipation through.
The modified circuit now is known as Class AB amplifier circuit. Less power consumption and lower heat. The conduction angle of class AB amplifier is somewhere between 180 o to 360 o depending upon the operating point selected.
An optional 10K POT can be added in series to the input for volume control. Its also larger in size. The high performance of an X1505 comes at a price.
A well designed Class-AB amp can often achieve lower distortion and better frequency response overall than many Class-A designs - especially those claiming low or no feedback. Class D is easier to live with though. From 0V to 07V the diodes are biased in conduction state where the transistors have no signal at the base terminal.
Despite claims to the contrary there is no intrinsic improvement in sound quality from Class-A. Class-AB is not a linear amplifier. Cross over distortion is not in zero crossing area Cross over distortion is at where.
A symmetrical BJT voltage-follower is presented which combines low harmonic distortion and high slew rate. Strong feedback is necessary to achieve good linearity. Unlike conventional class-AB voltage-followers the.
But there are also a number of gremlins that lurk within the AB architecture mostly in the form of bias instability and other thermally-related issues. Do the effects of high bias also apply to single-ended Class A bias. Inefficientmaximum possible efficiency is about 60.
Exponential in BJT quadratic in MOSFET. Class AB amplifiers have been the workhorses of the audio world thanks to their simplicity and their ability to deliver high power levels with low distortion. A signal with an amplitude-modulated envelope will be distorted significantly at this peak power level.
Distortion is typically between 10 and 20. Class AB amplifier Notes. The class AB push-pull output circuit is slightly less efficient than class B because it uses a small quiescent current flowing to bias the transistors just above cut off as shown in Fig.
The result will be that the circuit drifts into class AB operation where both transistors will be in a state of conduction part of the time. Conduction angle in Class-AB is between 180 and 360 and Efficiency is between 50 and 785 Class-AB has higher efficiency than Class-A at price of linearity. Transistors Q8 and Q5 must be fitted to a proper sink.
Use a 4 ohm20W speaker as the load. 551 but the crossover distortion created by the non-linear section of the transistors input characteristic curve near to cut off in class B is overcome. This may be acceptable for some situations but not for higher-quality audio designs.
Illustration of Class B and Class AB Push-Pull Inverting Amplifier Output current and voltage characteristics of the push-pull inverting amplifier RL 1kΩ-2V-1V 0V 1V 2V-2V -1V 0V 1V 2V-2mA-1mA 0mA 1mA 2mA vIN iD1 iD2 vG2 vG1 vOUT Class B push-pull inverting amplifier-1V 0V-2mA 1mA 2mA iD1 iD2 vG2 1 vOUT Class AB push-pull inverting. The small bias voltage given using diodes D 1 and D 2 as shown in the above figure helps the operating point to be above the cutoff point. This amplifier circuit can be operated from anything between 12 to 16 volts.
Lowest distortiontotal harmonic distortion plus noise THD N is less than 01 for high fidelity. This Class AB amplifier is a circuit made using the characteristics of both Class A and Class B amplifier circuits. 11 channels of good class ab could easily weigh 50kg and draw a significant amount of power.
Thus the diodes will continue to provide the same 14-volt bias voltage even though the transistors require less bias voltage due to heating. D Characteristic Comparison 22 Feature Class D Advanta ge Class AB Topology is inherently linear without feedback Output device is non-linear. By contrast an X1505 channel has that power rating but idles at about 100 watts.
Panasonic 65ex750 Sony HW40ES Projector Arcam 550 MKsound 150 DIY subs Buttkicker amp with Quake q10b.
Tidak ada komentar